Did you know that over a billion people worldwide live with some form of disability? Yet, accessibility has often been a secondary consideration in design. Thankfully, things are beginning to shift, with a growing recognition that accessibility benefits everyone, not just those with disabilities.
Artificial intelligence is at the forefront of this transformation, allowing us to go beyond simply meeting accessibility requirements and creating richer, more inclusive experiences. Tools like voice assistants and real-time captions are helping individuals engage with the world in ways that feel more intuitive and seamless.
Let’s explore some of the innovations leading the charge toward more accessible designs:
Voice Interaction: A Game Changer for Independence
Voice assistants such as Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri have transitioned from optional conveniences to essential tools, particularly for individuals with mobility challenges. These technologies empower users to control their environments — from adjusting lighting to setting reminders — all through voice commands.
For designers, this shift requires a fresh approach to navigation. Voice-first interfaces need to be clean, intuitive, and entirely touch-free. Traditional on-screen buttons and menus become secondary, as spoken words guide the user experience. Voice-driven design isn’t just about making tasks easier; it’s about creating independence.
In specialized areas like healthcare, voice-controlled devices are making a profound impact, enabling users to interact with medical equipment or call for assistance, all without physical movement. In education, children with physical disabilities can use voice technology to engage in lessons, fostering equal participation.
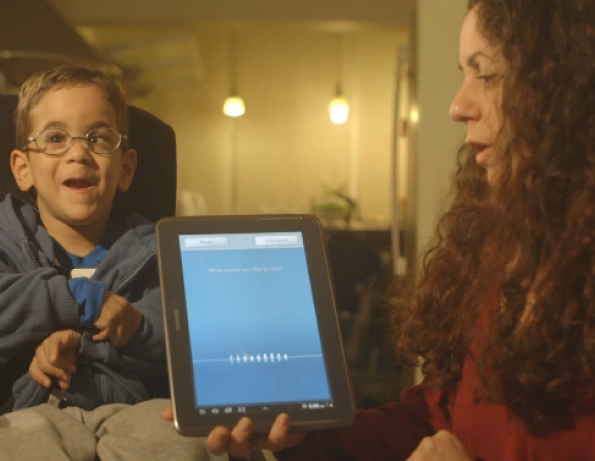
Take Voiceitt, for example. This app leverages AI to adapt to unique speech patterns, helping people with speech impairments communicate more effectively with mainstream voice assistants, overcoming traditional barriers.

Making Sound Accessible to All
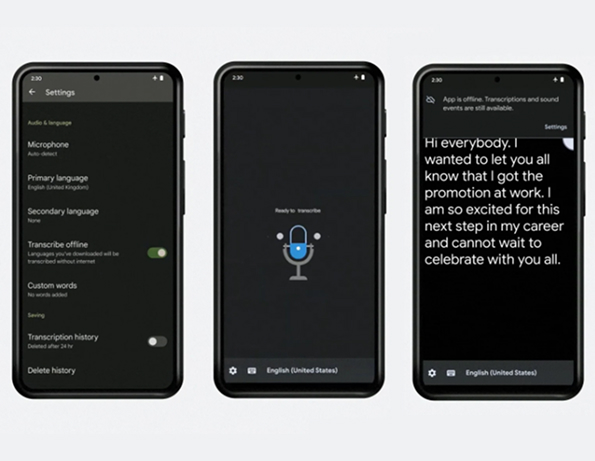
AI-powered real-time captioning is revolutionizing communication for individuals with hearing impairments. Tools like Google Live Transcribe instantly convert speech into written words, allowing users to follow conversations, meetings, and other audio-based interactions.
These tools are not only enhancing access to everyday communication but are also breaking down language barriers. Multi-language support, for instance, enables people to follow events or work meetings in real-time, no matter the language spoken.
AI is also making captioning more sophisticated by recognizing tone, emotion, and context, which adds depth to the captions, making them more meaningful than just text.
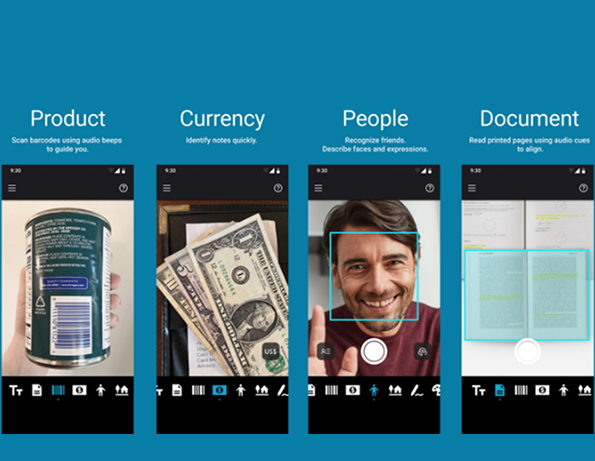
Object and Scene Recognition
AI apps like Seeing AI and Google Lookout are providing people with visual impairments the ability to better understand their surroundings. These tools go beyond object identification, helping users grasp the full context of a scene.
For example, Seeing AI can describe not just the objects in a person’s path but also important contextual information, such as identifying traffic or reading street signs, providing a richer, more immersive navigation experience.
Similarly, Google Lookout is assisting users in retail environments by reading product labels aloud, enabling them to shop independently.
In another innovation, Be My Eyes connects visually impaired users with sighted volunteers and, with AI advancements, now offers even more detailed scene descriptions, such as recognizing emotions on people’s faces or capturing the atmosphere of a room.
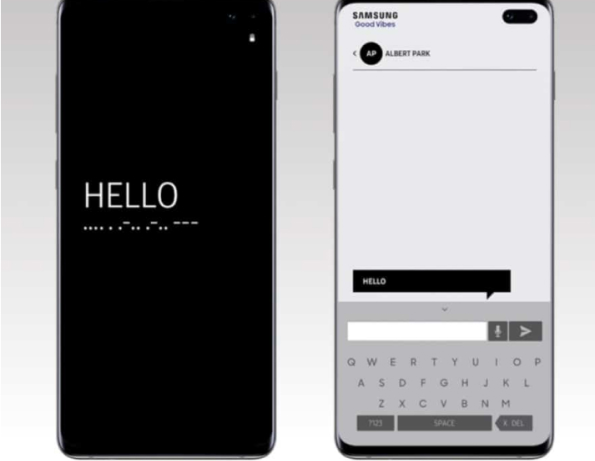
AI-Driven User-Centered Design: A New Era of Accessibility
Samsung’s Good Vibes app illustrates the power of AI in facilitating communication for users who are deaf-blind. The app translates text into Morse code vibrations, allowing users to interact with the world through touch patterns. This is an example of AI enhancing accessibility in an incredibly unique and practical way.